

In the push data consumption model, you write a method that fulfills the Sparkplug commands received ("Writes"). Rapid Toolkit for Sparkplug calls this method (pushes the data) when needed.
This is the more common data consumption model.
Your task as a developer is to provide the code for handling the Write request by either adding an event handler for the Write Event, or overriding the OnWrite Method. The code for handling the data push can be attached to each metric separately, or you can use a common code on the parent level - for example, a Sparkplug device object can have code that handles all Writes for the metrics contained in the device.
In order to indicate that you have handled the Write request, your code will call the HandleAndReturn Method on the event arguments object. Note that if you use the extension methods for configuration of metrics, the event handler added by the extension methods already does this for you.
The following picture illustrates how the push data consumption model works.
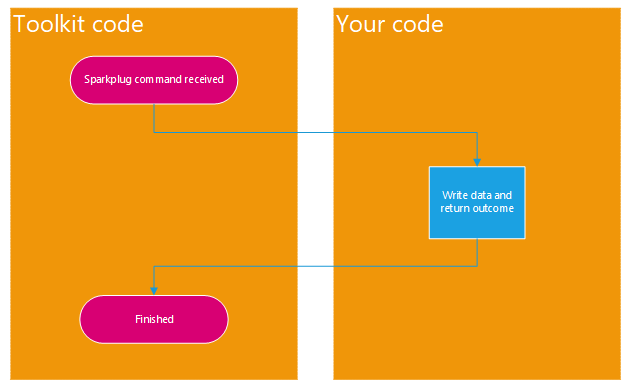
Rapid Toolkit for Sparkplug provides extension methods that allow you to define metrics that use the push data consumption model easily, without having to deal with method overrides, or handle events. This is described in the Sparkplug Metric Configuration article. Typically, you will use some overload of the WriteFunction, WriteValueAction or WriteValueFunction method to configure the metric for the push data consumption model. With these methods, you use .NET functions (Func<...,TResult> Delegate) or actions (Action Delegate) to specify the code that handles the request. The following example illustrates the use of the WriteValueAction method.
How do you choose between these three extension methods?
The following example illustrates the use of the WriteValueFunction method for a metric that forces its value to be within certain range.
If the metric should also support writing of the timestamp, you will use the WriteFunction method.
If your Sparkplug edge node or device has groups of metrics with basically the same behavior, you would probably want to specify the behavior just once, and not with every metric. In such case, you cannot use the extension methods for metric configuration (described above), and need to define the behavior by handling the Write Event, or overriding the OnWrite Method, on the parent level - in our example, the level of the edge node. The following examples illustrate these approaches.
Example: Examples - Sparkplug Edge Node - Writing different metrics by a single handler
Example: Examples - Sparkplug Edge Node - Metrics writing by method override
See Sparkplug Metric Data Type Considerations.
Sparkplug is a trademark of Eclipse Foundation, Inc. "MQTT" is a trademark of the OASIS Open standards consortium. Other related terms are trademarks of their respective owners. Any use of these terms on this site is for descriptive purposes only and does not imply any sponsorship, endorsement or affiliation.